What is REST API ?
November 20, 2024
Keywords: what are rest apis, rest api testing, rest api definition, what is a rest api, what is api and rest api
Read time: 5 minutes
Level: intermidiate
When building and testing modern web applications, APIs are foundational tools. Representational State Transfer (REST) has become a dominant architectural style for designing networked applications. This article dives into what REST APIs are, their importance, and considerations for testing, ensuring you can effectively leverage them in your projects.
What makes API a REST API?
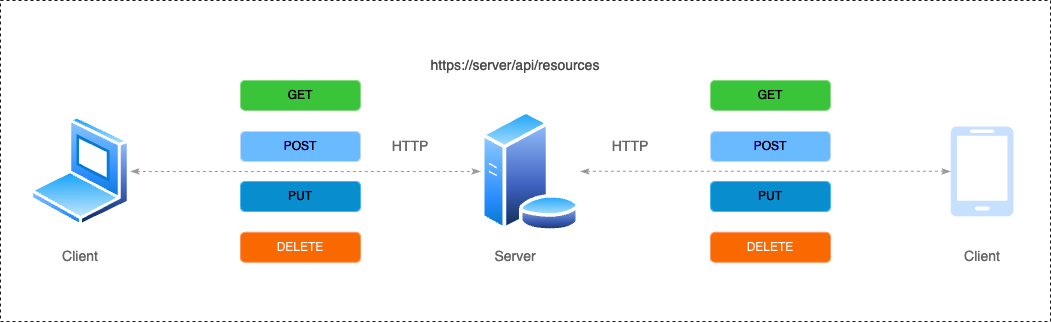
An API, or Application Programming Interface, allows two software applications to communicate with each other. It defines rules and protocols for interaction. A REST API, short for Representational State Transfer API, adheres to REST architectural principles, emphasizing stateless communication and leveraging standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Statelessness | Each request contains all information needed, with no reliance on server-side state. |
| Client-Server Model | Separates client concerns (UI, requests) from server concerns (data storage). |
| Cacheable | Responses are marked as cacheable or non-cacheable to optimize performance. |
| Uniform Interface | Uses standard HTTP verbs and consistent naming conventions for endpoints. |
| Layered System | Organizes components into layers, enhancing scalability, modularity, and security through intermediaries like proxies or gateways. |
For example, in a RESTful service, a GET request to https://api.example.com/users might fetch a list of users, while a POST request to the same endpoint would create a new user.
Definition and Use Cases
The REST API definition emphasizes scalability, simplicity, and flexibility. It is widely used in scenarios like:
- Microservices: Communication between distributed services.
- Mobile and Web Applications: Data retrieval and user interaction.
- Third-Party Integrations: Connecting external services like payment gateways or social media platforms.
Benefits
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Platform Independence | Works across multiple programming languages and platforms. |
| Scalability | Suitable for high-traffic environments. |
| Ease of Testing | Clear structure simplifies validation of endpoints. |
REST API Testing
REST API testing ensures that endpoints function correctly and adhere to specified requirements. Testing typically involves verifying the following aspects:
- Functional Testing: Checking if the API meets its functional specifications.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating response times and throughput under load.
- Security Testing: Ensuring sensitive data is protected and endpoints are secure.
- Data Validation: Verifying that data formats (JSON, XML) match the schema.
Common tools for testing include Testlemon, Postman, SoapUI, and automated frameworks like REST-assured for Java. Testers often focus on:
- HTTP Response Codes: Validating codes like 200 (Success), 404 (Not Found), and 500 (Server Error).
- Headers and Payloads: Ensuring they match expected formats and content.
- Authentication: Testing mechanisms like OAuth and API keys.
The Role in Modern Development?
REST APIs are crucial for connecting systems in modern software, promoting modularity and best practices like separation of concerns. They help senior developers design scalable solutions and aid testers with their predictable structure for efficient debugging and validation.
In summary, understanding REST APIs, testing their robustness, and applying them effectively are vital for building resilient applications. Leveraging tools and methods for API testing can streamline development and QA workflows.
Mastering APIs enables developers and testers to deliver applications that excel in usability, reliability, and performance.